Overview
Flat feet, also known as ?fallen arches? are often viewed as problematic simply because they look abnormal, the main arch of the foot, the medial longitudinal arch, has collapsed. Though flat feet are by no means normal, they are often the result of some other underlying condition or weakness rather than a problem with the actual arch itself that has collapsed. Conventional treatment involving foot support either via supportive footwear, orthotics, or some other bracing system is usually more disadvantageous than beneficial and surgery is rarely the answer.

Causes
Flatfoot can have many different causes. It could be a weakness or a structural abnormality you?ve had since birth. It could also mean that tendonitis, damage to the connective tissues, arthritis, or nerve problems have affected the structures in your feet. Even wearing unsupportive footwear can lead to weakness and arch pain. Whatever the cause, many conservative, noninvasive treatments exist to help relieve and eliminate your discomfort.
Symptoms
The muscle imbalance around the foot and ankle gives rise to a typical pattern of deformity in addition to the high arch (known as cavus). The bone under the big toe (called the first metatarsal) can become very prominent and the toes can curl or clench like a fist (called claw toes). Excessive amount of weight may be placed on the ball and heel of the foot, which can lead to the ankle weakening and giving way (this is referred to as ankle instability) and soreness. Calluses and sometimes stress fractures may occur where the foot is exposed to extra friction or pressure, such as on the outer (or lateral) border of the foot.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a plantar plate tear can often be challenging due to the complex nature of the anatomy of the foot. Careful history taking and an examination of the area of pain is required to determine the extent and cause of the tear. If necessary, further investigations such as x-rays or diagnostic ultrasound may be ordered by your podiatrist to help evaluate the severity of the problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Doctors commonly prescribe shoe inserts, or orthotics, to support the arch. These devices make walking and standing more comfortable for a person with fallen arches, reports the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Orthotics are typically worn with closed shoes. They are available over-the-counter or can be custom-made.

Surgical Treatment
Foot surgery is difficult, especially when large amounts of deformity correction are needed. The ability to bring the foot into a new position may not be lasting, even if everything looks perfect in the operating room. The goal is to provide improved position and function of the foot and ankle. In some patients with very severe deformity, the goal is a foot that functions well in a brace. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Particular complications associated with cavus foot surgery include incomplete correction of deformity, return of deformity and incomplete fusion.
Prevention
The best method for preventing plantar fasciitis is stretching. The plantar fascia can be stretched by grabbing the toes, pulling the foot upward and holding for 15 seconds. To stretch the calf muscles, place hands on a wall and drop affected leg back into a lunge step while keeping the heel of the back leg down. Keep the back knee straight for one stretch and then bend the knee slightly to stretch a deeper muscle in the calf. Hold stretch for 15 seconds and repeat three times.
Flat feet, also known as ?fallen arches? are often viewed as problematic simply because they look abnormal, the main arch of the foot, the medial longitudinal arch, has collapsed. Though flat feet are by no means normal, they are often the result of some other underlying condition or weakness rather than a problem with the actual arch itself that has collapsed. Conventional treatment involving foot support either via supportive footwear, orthotics, or some other bracing system is usually more disadvantageous than beneficial and surgery is rarely the answer.

Causes
Flatfoot can have many different causes. It could be a weakness or a structural abnormality you?ve had since birth. It could also mean that tendonitis, damage to the connective tissues, arthritis, or nerve problems have affected the structures in your feet. Even wearing unsupportive footwear can lead to weakness and arch pain. Whatever the cause, many conservative, noninvasive treatments exist to help relieve and eliminate your discomfort.
Symptoms
The muscle imbalance around the foot and ankle gives rise to a typical pattern of deformity in addition to the high arch (known as cavus). The bone under the big toe (called the first metatarsal) can become very prominent and the toes can curl or clench like a fist (called claw toes). Excessive amount of weight may be placed on the ball and heel of the foot, which can lead to the ankle weakening and giving way (this is referred to as ankle instability) and soreness. Calluses and sometimes stress fractures may occur where the foot is exposed to extra friction or pressure, such as on the outer (or lateral) border of the foot.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a plantar plate tear can often be challenging due to the complex nature of the anatomy of the foot. Careful history taking and an examination of the area of pain is required to determine the extent and cause of the tear. If necessary, further investigations such as x-rays or diagnostic ultrasound may be ordered by your podiatrist to help evaluate the severity of the problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Doctors commonly prescribe shoe inserts, or orthotics, to support the arch. These devices make walking and standing more comfortable for a person with fallen arches, reports the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Orthotics are typically worn with closed shoes. They are available over-the-counter or can be custom-made.

Surgical Treatment
Foot surgery is difficult, especially when large amounts of deformity correction are needed. The ability to bring the foot into a new position may not be lasting, even if everything looks perfect in the operating room. The goal is to provide improved position and function of the foot and ankle. In some patients with very severe deformity, the goal is a foot that functions well in a brace. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Particular complications associated with cavus foot surgery include incomplete correction of deformity, return of deformity and incomplete fusion.
Prevention
The best method for preventing plantar fasciitis is stretching. The plantar fascia can be stretched by grabbing the toes, pulling the foot upward and holding for 15 seconds. To stretch the calf muscles, place hands on a wall and drop affected leg back into a lunge step while keeping the heel of the back leg down. Keep the back knee straight for one stretch and then bend the knee slightly to stretch a deeper muscle in the calf. Hold stretch for 15 seconds and repeat three times.






 Achilles tendon rupture are common. Most athletes describe a sudden acute event with an associated popping sensation and pain in the Achilles tendon. They often think that they have been kicked or struck in the calf. It is important to get prompt treatment and to be placed in an equinous cast (a cast with the foot in a pointed position). More definitive treatment options can be discussed after this has occurred.
Achilles tendon rupture are common. Most athletes describe a sudden acute event with an associated popping sensation and pain in the Achilles tendon. They often think that they have been kicked or struck in the calf. It is important to get prompt treatment and to be placed in an equinous cast (a cast with the foot in a pointed position). More definitive treatment options can be discussed after this has occurred.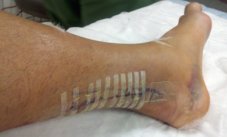
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
