Overview
Leg length discrepancy is a condition where the length of one leg is different than the other (shorter or longer) because of either or both a functional (muscle/posture) or structural (bone/cartilage) abnormality. In the specific a functional leg length occurs when your legs are the same, but another condition such as pelvic tilt or piriformis shortening creates the appearance of one leg being longer or shorter than the other. A structural leg length inequality it means that there is a true difference. Osteopaths, chiropractors and physiotherapist should be able to determine the degree of leg length inequality using visual inspection and manual tests.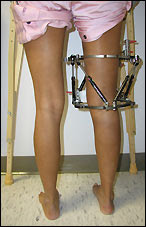
Causes
Leg length discrepancies can be caused by: hip and knee replacements, lower limb injuries, bone diseases, neuromuscular issues and congenital problems. Although discrepancies of 2 cm or less are most common, discrepancies can be greater than 6 cm. People who have LLD tend to make up for the difference by over bending their longer leg or standing on the toes of their shorter leg. This compensation leads to an inefficient, up and down gait, which is quite tiring and over time can result in posture problems as well as pain in the back, hips, knees and ankles.
Symptoms
The effects vary from patient to patient, depending on the cause of the discrepancy and the magnitude of the difference. Differences of 3 1/2 to 4 percent of the total length of the lower extremity (4 cm or 1 2/3 inches in an average adult), including the thigh, lower leg and foot, may cause noticeable abnormalities while walking and require more effort to walk. Differences between the lengths of the upper extremities cause few problems unless the difference is so great that it becomes difficult to hold objects or perform chores with both hands. You and your physician can decide what is right for you after discussing the causes, treatment options and risks and benefits of limb lengthening, including no treatment at all. Although an LLD may be detected on a screening examination for curvature of the spine (scoliosis), LLD does not cause scoliosis. There is controversy about the effect of LLD on the spine. Some studies indicate that people with an LLD have a greater incidence of low back pain and an increased susceptibility to injuries, but other studies refute this relationship.
Diagnosis
Infants, children or adolescents suspected of having a limb-length condition should receive an evaluation at the first sign of difficulty in using their arms or legs. In many cases, signs are subtle and only noticeable in certain situations, such as when buying clothing or playing sports. Proper initial assessments by qualified pediatric orthopedic providers can reduce the likelihood of long-term complications and increase the likelihood that less invasive management will be effective. In most cases, very mild limb length discrepancies require no formal treatment at all.
Non Surgical Treatment
After the leg length discrepancy has been identified it can be categorized in as structural or functional and appropriate remedial action can be instigated. This may involve heel lifters or orthotics being used to level up the difference. The treatment of LLD depends on the symptoms being experienced. Where the body is naturally compensating for the LLD (and the patient is in no discomfort), further rectifying action may cause adverse effects to the biomechanical mechanism of the body causing further injury. In cases of functional asymmetry regular orthotics can be used to correct the geometry of the foot and ground contact. In structural asymmetry cases heel lifts may be used to compensate for the anatomic discrepancy.

leg length discrepancy test
Surgical Treatment
Surgical operations to equalize leg lengths include the following. Shortening the longer leg. This is usually done if growth is already complete, and the patient is tall enough that losing an inch is not a problem. Slowing or stopping the growth of the longer leg. Growth of the lower limbs take place mainly in the epiphyseal plates (growth plates) of the lower femur and upper tibia and fibula. Stapling the growth plates in a child for a few years theoretically will stop growth for the period, and when the staples were removed, growth was supposed to resume. This procedure was quite popular till it was found that the amount of growth retarded was not certain, and when the staples where removed, the bone failed to resume its growth. Hence epiphyseal stapling has now been abandoned for the more reliable Epiphyseodesis. By use of modern fluoroscopic equipment, the surgeon can visualize the growth plate, and by making small incisions and using multiple drillings, the growth plate of the lower femur and/or upper tibia and fibula can be ablated. Since growth is stopped permanently by this procedure, the timing of the operation is crucial. This is probably the most commonly done procedure for correcting leg length discrepancy. But there is one limitation. The maximum amount of discrepancy that can be corrected by Epiphyseodesis is 5 cm. Lengthening the short leg. Various procedures have been done over the years to effect this result. External fixation devices are usually needed to hold the bone that is being lengthened. In the past, the bone to be lengthened was cut, and using the external fixation device, the leg was stretched out gradually over weeks. A gap in the bone was thus created, and a second operation was needed to place a bone block in the gap for stability and induce healing as a graft. More recently, a new technique called callotasis is being use. The bone to be lengthened is not cut completely, only partially and called a corticotomy. The bone is then distracted over an external device (usually an Ilizarov or Orthofix apparatus) very slowly so that bone healing is proceeding as the lengthening is being done. This avoids the need for a second procedure to insert bone graft. The procedure involved in leg lengthening is complicated, and fraught with risks. Theoretically, there is no limit to how much lengthening one can obtain, although the more ambitious one is, the higher the complication rate.
Leg length discrepancy is a condition where the length of one leg is different than the other (shorter or longer) because of either or both a functional (muscle/posture) or structural (bone/cartilage) abnormality. In the specific a functional leg length occurs when your legs are the same, but another condition such as pelvic tilt or piriformis shortening creates the appearance of one leg being longer or shorter than the other. A structural leg length inequality it means that there is a true difference. Osteopaths, chiropractors and physiotherapist should be able to determine the degree of leg length inequality using visual inspection and manual tests.

Causes
Leg length discrepancies can be caused by: hip and knee replacements, lower limb injuries, bone diseases, neuromuscular issues and congenital problems. Although discrepancies of 2 cm or less are most common, discrepancies can be greater than 6 cm. People who have LLD tend to make up for the difference by over bending their longer leg or standing on the toes of their shorter leg. This compensation leads to an inefficient, up and down gait, which is quite tiring and over time can result in posture problems as well as pain in the back, hips, knees and ankles.
Symptoms
The effects vary from patient to patient, depending on the cause of the discrepancy and the magnitude of the difference. Differences of 3 1/2 to 4 percent of the total length of the lower extremity (4 cm or 1 2/3 inches in an average adult), including the thigh, lower leg and foot, may cause noticeable abnormalities while walking and require more effort to walk. Differences between the lengths of the upper extremities cause few problems unless the difference is so great that it becomes difficult to hold objects or perform chores with both hands. You and your physician can decide what is right for you after discussing the causes, treatment options and risks and benefits of limb lengthening, including no treatment at all. Although an LLD may be detected on a screening examination for curvature of the spine (scoliosis), LLD does not cause scoliosis. There is controversy about the effect of LLD on the spine. Some studies indicate that people with an LLD have a greater incidence of low back pain and an increased susceptibility to injuries, but other studies refute this relationship.
Diagnosis
Infants, children or adolescents suspected of having a limb-length condition should receive an evaluation at the first sign of difficulty in using their arms or legs. In many cases, signs are subtle and only noticeable in certain situations, such as when buying clothing or playing sports. Proper initial assessments by qualified pediatric orthopedic providers can reduce the likelihood of long-term complications and increase the likelihood that less invasive management will be effective. In most cases, very mild limb length discrepancies require no formal treatment at all.
Non Surgical Treatment
After the leg length discrepancy has been identified it can be categorized in as structural or functional and appropriate remedial action can be instigated. This may involve heel lifters or orthotics being used to level up the difference. The treatment of LLD depends on the symptoms being experienced. Where the body is naturally compensating for the LLD (and the patient is in no discomfort), further rectifying action may cause adverse effects to the biomechanical mechanism of the body causing further injury. In cases of functional asymmetry regular orthotics can be used to correct the geometry of the foot and ground contact. In structural asymmetry cases heel lifts may be used to compensate for the anatomic discrepancy.

leg length discrepancy test
Surgical Treatment
Surgical operations to equalize leg lengths include the following. Shortening the longer leg. This is usually done if growth is already complete, and the patient is tall enough that losing an inch is not a problem. Slowing or stopping the growth of the longer leg. Growth of the lower limbs take place mainly in the epiphyseal plates (growth plates) of the lower femur and upper tibia and fibula. Stapling the growth plates in a child for a few years theoretically will stop growth for the period, and when the staples were removed, growth was supposed to resume. This procedure was quite popular till it was found that the amount of growth retarded was not certain, and when the staples where removed, the bone failed to resume its growth. Hence epiphyseal stapling has now been abandoned for the more reliable Epiphyseodesis. By use of modern fluoroscopic equipment, the surgeon can visualize the growth plate, and by making small incisions and using multiple drillings, the growth plate of the lower femur and/or upper tibia and fibula can be ablated. Since growth is stopped permanently by this procedure, the timing of the operation is crucial. This is probably the most commonly done procedure for correcting leg length discrepancy. But there is one limitation. The maximum amount of discrepancy that can be corrected by Epiphyseodesis is 5 cm. Lengthening the short leg. Various procedures have been done over the years to effect this result. External fixation devices are usually needed to hold the bone that is being lengthened. In the past, the bone to be lengthened was cut, and using the external fixation device, the leg was stretched out gradually over weeks. A gap in the bone was thus created, and a second operation was needed to place a bone block in the gap for stability and induce healing as a graft. More recently, a new technique called callotasis is being use. The bone to be lengthened is not cut completely, only partially and called a corticotomy. The bone is then distracted over an external device (usually an Ilizarov or Orthofix apparatus) very slowly so that bone healing is proceeding as the lengthening is being done. This avoids the need for a second procedure to insert bone graft. The procedure involved in leg lengthening is complicated, and fraught with risks. Theoretically, there is no limit to how much lengthening one can obtain, although the more ambitious one is, the higher the complication rate.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
